Python OOP
python object oriented programming

In this article
Related Articles
- How to download Python, best IDE and ready to code
- Python Basic
- Flask Quickstart
- How to create a website with Python Flask
- Jinja Templates
- RESTFUL API
Python is one of the object oriented programming language. Class are created method and properties. if we create class, we can use more than once that class with creating object.
Class ( class classname: )
Teacher class
class Teacher:
passObject ( object = class( ) )
Creating an object named Emma
class Teacher:
pass
emma = Teacher()In a class, we can add properties and methods.
class Teacher:
#property
subject = "Math"
#method
def teach(self):
return f"teaching {self.subject}"
emma = Teacher()
print(emma.subject)
print(emma.teach())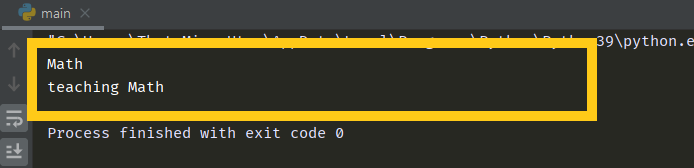
dot Operator
Object connects with its own properties and methods by dot operator.(emma.subject)
self parameter
parameter self means its own properties. ( def teach(self) )
Constructor ( def __init__(self) )
def __init__(self) is constructor function. constructor function give you starting values after you create an object. In python, constructor is used to initialize object values. And that function is called automatically after you created an object.
class Teacher:
def __init__(self):
print("this is constructor function")
def teach(self):
return f"teaching"
# at the same time you create an object, constructor is called
emma = Teacher()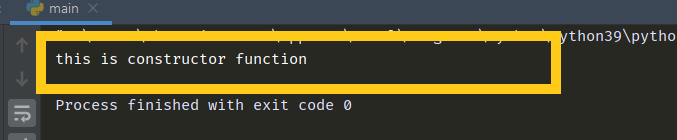
And it is used to assign values
class Teacher:
def __init__(self, subject):
self.subject = subject
def teach(self):
return f"teaching {self.subject}"
emma = Teacher("Math")
print(emma.teach())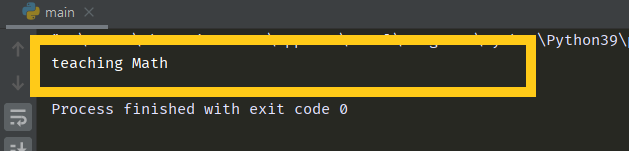
Inheritance
Child class inherits from Parent class
class Parent:
def __init__(self):
self.eye_color = "black"
class Child(Parent):
pass
sophia = Child()
print(sophia.eye_color)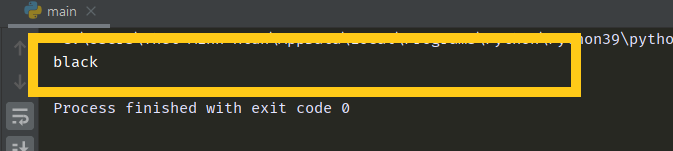
class Parent:
def __init__(self, hair_color):
self.hair_color = hair_color
self.eye_color = "gray"
class Child(Parent):
def __init__(self, hair_color):
super().__init__(hair_color)
self.age:int
def get_all(self):
print(f"hair color is {self.hair_color}")
print(f"eye color is {self.eye_color}")
print(f"age is {self.age}")
sophia = Child("black")
sophia.age = 12
sophia.get_all()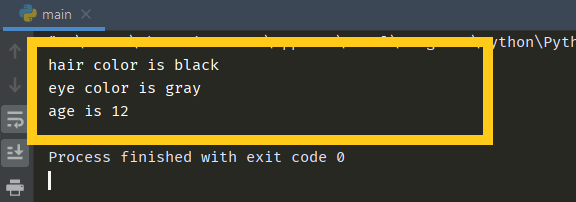
Super Function ( super( ) )
super function return parent class
super().__init__()Class B inheritance from Class A
class a():
def __init__(self):
self.num = 3
self.total = 10
class b(a):
def __init__(self):
self.shape = 'circle'
object_b = b()
print(object_b.num)Result
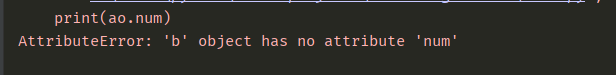
Class B inheritance from Class A and create own shape value
class a():
def __init__(self):
self.num = 3
self.total = 10
class b(a):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.shape = 'circle'
object_b = b()
print(object_b.num)Result

